Aplicación de Diseños de Experimentos en la Optimización de un Método por Microextracción en fase Sólida-Espacio de Cabeza para la Determinación del 4- Metilnitrosamino) -1-(3-Piridil)-1-Butanol (NNAL) en Muestras de Orina.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.29105/qh7.3-109Keywords:
GC-MS, NNAL, SPME, orina, tabacoAbstract
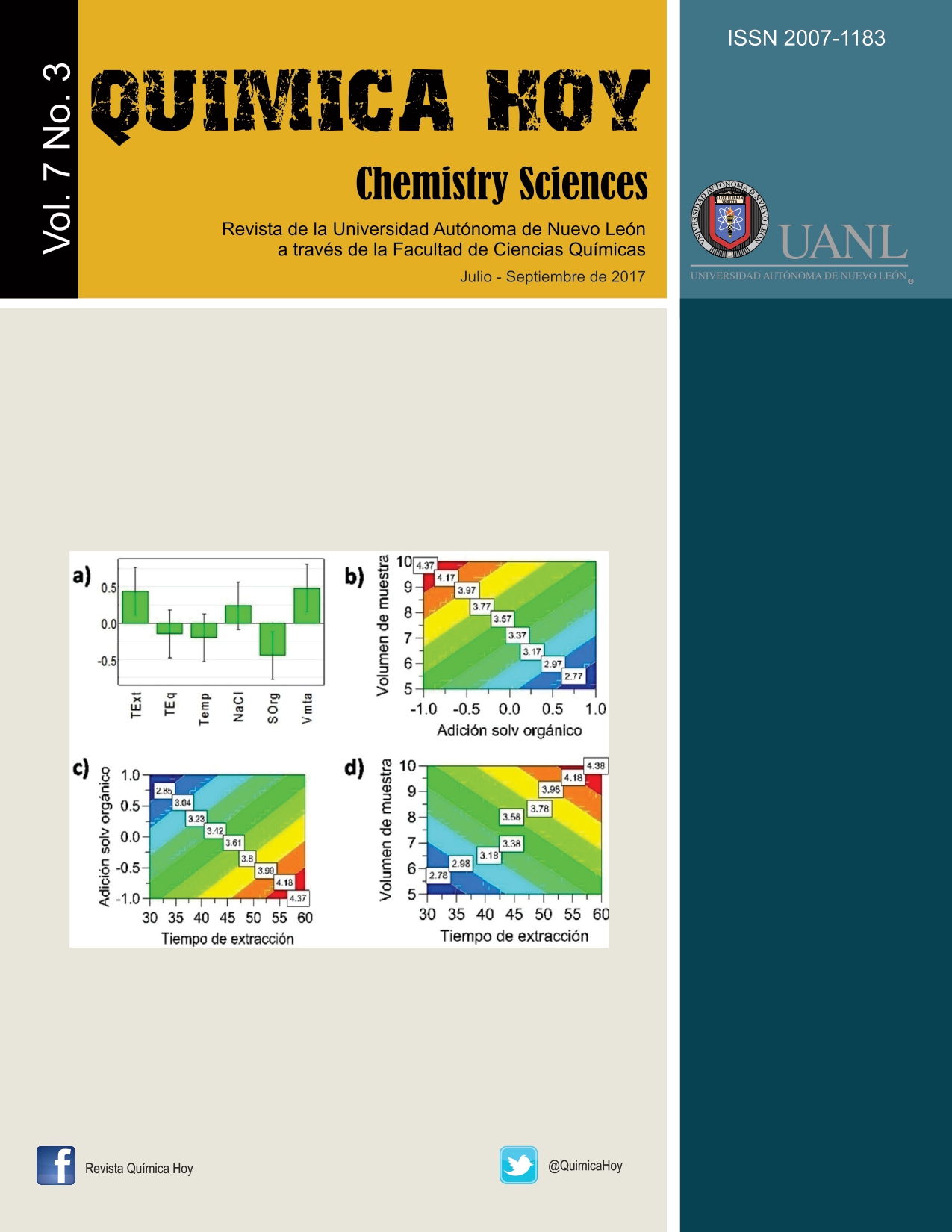
Se desarrolló un método de microextracción en fase sólida modalidad headspace (HS-SPME) seguido de un análisis por cromatografia de gases-espectrometria de masas para la determinación de NNAL en muestras de orina. Se probaron cuatro fibras comerciales para el desarrollo del método de SPME, se observó que la fibra de DivinilbencenoPolidimetilsiloxano de 65 µm presentó un mejor desempeño de extracción. Los parámetros que afectan el desempeño del proceso de la SPME fueron evaluados con la ayuda de diseños de experimentos, tanto Plackett- Burman (PB) así como Diseños Simplex. Las variables estudiadas del proceso de extracción fueron el volumen de muestra, adición de sal, adición de solvente orgánico, velocidad de agitación, temperatura de extracción, tiempo de extracción y tiempo de preequilibrio. Las variables que presentaron influencia en el proceso de extracción fueron el tiempo de extracción, el volumen de muestra y la adición de metanol como solvente orgánico. El método desarrollado presentó un 6.7 % DER, por lo que la precisión mostrada es aceptable.
Downloads
References
-[1] Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS), "Informe OMS sobre la epidemia mundial de tabaquismo, 2008: plan de medidas MPOWER,"Francia, 2008.
-[2] C. M. Guerrero-López, J . A. Muflos-Henández,M . C, B. S. De Miera-Juárez, L. M. Reynales-Shigematsu, and D. C, "Consumo de tabaco, mortalidad y política fiscal en México," Salud Publica Mex., 2013, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 276-281. DOI: https://doi.org/10.21149/spm.v55s2.5125
-[3] Instituto Nacional de Psiquiatría Ramón de la Fuente Muñiz; Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública; Secretaría de Salud, "Encuesta Nacional de Adicciones 2011: Reporte de Tabaco," INPRFM, México DF, México, 2012.
-[4] A. Pérez Trullén, C . Bartolomé, M . Barrueco, l. Herrero, and C. Jiménez, "Nuevas perspectivas en el diagnóstico y evolución del consumo de tabaco: marcadores de exposición,"Prev Tab,2 006, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 164-173.
-[5] Y. Xia, J. T. Bemert, R. B. Jain, D. L. Ashley, and J. L. Pirkle, "Tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-l-butanol (NNAL) in smokers in the United States: NHANES2 007-2008.," Biomarkers,2011,vol. 16, no. 2,pp. 112-119. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/1354750X.2010.533288
-[6] S. S. Hecht and D. Hoffmann, "Tobacco-specific nitrosamines, an important group of carcinogens in tobacco and tobacco smoke,"Carcinogenesis, 1988, vol. 9,no.6,pp.875-884. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/9.6.875
-[7] Intemational Agency for Research on Cancer, IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Smokeless Tobacco and Sorne Tobaccospecific N -Nitrosamines, vol. 89. Lyon, France: Intenational Agency for Research on Cancer, 2007.
-[8] E. Schrader, K . Hirsch-Emest,E . Scholz, G . F. Kahl, and H. Foth, "Metabolism of 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3pyridyl}-l-butanonen (NNK) in primary cultures of rat alveolar type II cells," Drug Metab. Dispos., 2000, vol. 28,no.2,pp. 180-185.
-[9] Q. Ren, S. E. Murphy, and Z. Zheng, "O Glucuronidation of the lung carcinogen 4- ( methylnitrosamino) -1- ( 3-pyridyl) -1-butanol ( NNAL ) by human UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases 2B7 and 1A9," Drug Metab. Dispos., 2000, vol. 28, no. 11, pp. 1352-1360.
-[10] D. Wiener,D . R. Doerge, J. Fang, P. Upadhyaya, and P. Lazarus, "characterization of N- Glucuronidation of the lung carcinogen 4 -(methylnitrosamino) -1-( 3-pyridyl) -1-butanol ( NNAL) in human liver : Importance of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase 1A4," Drug Metab. Dispos., 2004, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 72-79. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.32.1.72
-[11] L. Nováková and H. Vlcková, "A review of current trends and advances in modem bioanalytical methods: chromatography and sample preparation.," Anal. Chim. Acta, 2009, vol. 656, no. l-2,pp.8-35. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2009.10.004
-[12] C. Yagüe, S. Bayarri, R. Lázaro, P. Conchello, A. Ariño, and A. Herrera, "Multiresidue Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Milk by Gas Chromatography with Electron-Capture Detection after Extraction by Matrix Solid-Phase Dispersion," J. AOAC Int., 2001, vol. 84, no. 5, pp. 1561-1568. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/84.5.1561
-[13] W. M. Munett, K. Levsen, R. Borlak, J. Wu, and J. Pawliszyn, "Automated In-Tube Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled with HPLC for the Determination of N-Nitrosamines in Cell Cultures," Anal. Chem.,2002, vol. 74,no. 7,pp. 1695-1701. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ac015723v
-[14] K. a Shah and H. T. Karnes, "A review of the analysis of tobacco-specific nitrosamines in biological matrices.," Crit. Rev. Toxicol ., 2010 ,vol. 40,no.4,pp.305-327. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/10408440903394435
-[15] S. G. Carmella, X. Ming, N. Olvera, C. Brookmeyer, A. Yoder, and S. S. Hecht, "High throughput liquid and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assays for tobacco-specific nitrosamine and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon metabolites associated with lung cancer in smokers.," Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2013, vol. 26, no. 8,pp.1209-1217. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/tx400121n
-[16] J. T. Bernert, R. B. Jain, J. L. Pirkle, L. Wang, B. B. Miner, and E. J. Sampson, "Urinary tobaccospecific nitrosamines and 4-aminobiphenyl hemoglobin adducts measured in smokers of either regular or light cigarettes.," Nicotine Tob. Res., 2005, vol. 7,no. 5,pp. 729-738. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/14622200500259762
-[17] S. G. Carmena, S. Han,A. Fristad, Y.Y ang, and S. S. Hecht, "Analysis of Total 4-(Methylnitrosamino) 1-(3-Pyridyl)- l -Butanol (NNAL) in Human Urine," Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev., 2003, vol.12,no. ll,pp.1257-1261.
-[18] R. Van Orden, "Advantages and Disadvantages of High-end Mass Spectrometry in a Toxicology Lab," Advantages and disadvantages of High-end mass spectrometry in a Toxicology lab., 2013. [Online]. A v a i l a b l e http:/ /www.chem.agilent.com/Library/slidepresent ation/Public/Advantages_ disadvantages_ of_ Highend_ MS_ in_ Toxicology_ Lab.pdf.
-[19] G. D. Byrd and M. W. Ogden, "Liquid chromatographic/tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of the tobaccospecific nitrosamine metabolite NNAL in smokers' urine.," J. Mass Spectrom., 2003, vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 98-107. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.406
-[20] S. G. Carmena, S. Akerkar, and S. S. Hecht, "Metabolites of the Tobacco-specific Nitrosamine4-(methylnitrosamino) -1-(3-pyridyl) butanone in Smokers' Urine," Cancer Res., 1993, vol. 53,pp. 721-724.
-[21] "METHOD 8000D - DETERMINATIVE CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATIONS 8000d.pdf." [Online]. Available: http://www3.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethod s/sw846/pdfs/8000d.pdf.[ Accessed: 15-Jan-2016].
-[22] "SPME StableFlex TM fiber assortment kit for use with manual holder I Sigma-Aldrich." [Online]. A v a i l a b I e http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sup elco/57550u?lang=es®ion=MX.[ Accessed: 17Aug-2017].
-[23] "Analysisadvisor,Modde."Umetrics,2015.
-[24] "Diseños de Plackett-Burman." [Online]. Available: http :/ /support.minitab.com/esmx/mini tab/ 1 7 /topic-library/modelingstatistics/doe/factorial-designs/plackett-burmandesigns/. [Accessed: 13-Jan-2016].
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2017 Magdalena Escobar-Saucedo, Noemí Waksman Minsky, Ma. de la Luz Salazar-Cavazos, Rocío Castro Ríos, Augusto Rojas Martínez, J. Ricardo Lucio-Gutiérrez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.